Gorilla Treks - Your Gorilla Tour Specialist
Mountain Gorillas
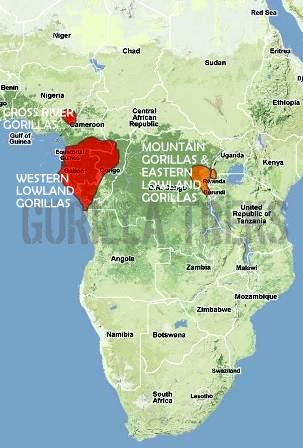
There are two species of gorilla -the eastern and western gorilla. Within each species of gorilla, there are two subspecies. The western gorilla are divided into western lowland gorilla and Cross River gorilla, while the eastern gorilla are divided into eastern lowland gorilla and mountain gorilla. Gorillas live only in equatorial Africa.
|
Subspecies
|
Scientific
Name
|
Population
|
Range
|
Appearance
|
| Western Lowland | Gorilla gorilla gorilla |
150,000
|
Congo, Guinea, Gabon, Angola, Nigeria, Central African Republic, Cameroon | brownish-grayish fur, smaller (400 lbs), more slender bodies |
| Cross River | Gorilla gorilla diehl |
300
|
Nigeria, Cameroon | smaller skull, shorter limbs |
| Eastern Lowland | Gorilla beringei graueri |
5,000
|
Uganda, Rwanda, Congo | darker black fur, larger (500 lbs) |
| Mountain | Gorilla beringei beringei |
800
|
Uganda, Rwanda, Congo | larger (500 lbs), taller, pointed head, longer and thicker coat |
Both species of gorilla are endangered. Throughout the years, gorillas were hunted for food, poached for pets and souvenirs, and displaced from habitat destruction. As a result of human actions, gorilla populations have rapidly dwindled. Most believed to that wild gorillas were candidates for extinction. Due to recent conservation, gorilla populations have thus far been saved.
Mountain gorillas are located in high altitudes, in the Virunga range of volcanic mountains on the borders of the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), Rwanda and Uganda, and in the Bwindi Impenetrable National Park in Uganda. The Virunga population is estimated to be 500 gorillas. They are found in the southern part of Virunga National Park, DRC, and the Volcanoes National Park, northern Rwanda, Mgahinga National Park, and southwestern Uganda. An estimated 300 mountain gorilla live in the Bwindi Impenetrable National Park.
Only 800 mountain gorillas are alive today, a result of vigilant protection efforts by governments. There are no mountain gorillas in zoos; they do not survive in captivity.
Mountain gorillas are social animals, living together in small groups, though some families can be as large as 30 individuals. Each family unit usually is comprised of a dominant adult male, several adult females, young males and females, and their offspring. Gorillas share 98% of human DNA. They are very intelligent creatures that exhibit human emotions. Though the physical power of gorillas is obvious, gorillas are gentle and even shy primates. They rarely fight within their family units. Gorillas do however battle other gorilla groups to defend their families and territories, which range about 10-15 square miles.
 Gorillas
are mainly herbivores. They eat a variety of plants, including roots, shoots, bark and pulp. They also eat fruits and invertebrates.
They spend about six hours a day eating.
Gorillas
are mainly herbivores. They eat a variety of plants, including roots, shoots, bark and pulp. They also eat fruits and invertebrates.
They spend about six hours a day eating.
The rest of a gorilla's day is spent travelling or sleeping. Though gorillas can climb trees, they spend most of their time on the ground. They tend to travel less than one kilometer per day. The normal territory of each gorilla family is about 20 square kilometers. Mountain gorillas, except for children who sleep with their mothers, each build their own nest out of vegetation every night for sleeping.
Gorillas reproduce slowly. Female gorillas give birth to a baby once every four years. The preganancy lasts almost nine months. The mortality rate for baby gorillas is greater than 30%, due to diseases and accidents. Newborn gorillas
are small and fragile. They weigh about five pounds and must be cared for at all times. After three months, the baby gorilla can walk on its own but usually ride on their mother's back until they are three years old. By two years old, they are able to eat plants. Baby gorillas are gradually weaned at about three years old.
Young male and female gorillas are classed as juvenile between the ages
of about two and six years. They spend most of their time playing and climbing trees. At age six, mountain gorillas are about four feet tall
and weigh about 150 lbs.
 Females
mature at about age six, and give birth between 10 to 12 years old. At full size, females weight 250-300 lbs.
Females
mature at about age six, and give birth between 10 to 12 years old. At full size, females weight 250-300 lbs.
Males continue to grow both in size and weight and reach maturity at ten years old. Between six and 10 years old, male gorillas are called blackbacks, referring to their uniform black coat. A full size male is five-six feet tall and weighs 450-500 lbs.
At maturity, male mountain gorillas develop a patch of grayish
or silver-colored hair on their backs, which is where the name
silverback comes from. At this time, the adult male leaves the family and will wander alone or join other males
for some time, before attracting females to start their own family.
The life span of mountain gorillas in the wild is 25 to 30
years.
- Bwindi Gorilla Trek:
3 days / $1,960 - Volcanoes Gorilla Trek:
3 days / $1,910 - Rwanda Gorilla & Monkeys: 4 days / $2,200
- Rwanda Gorilla Safari (2X): 4 days / $3,000
- Bwindi/Kibale Safari:
5 days / $2,570 - Bwindi/Queen Eliz.:
5 days / $2,670 - Uganda/Rwanda Gorilla: 5 days / $3,290
- Rwanda/Uganda Gorilla: 5 days / $3,100
- 6 day Uganda Safari:
6 days / $3,060 - 7 day Uganda Safari:
7 days / $3,470 - 8 day Uganda Safari:
8 days / $3,570 - 9 day Uganda Safari:
9 days / $4,260


